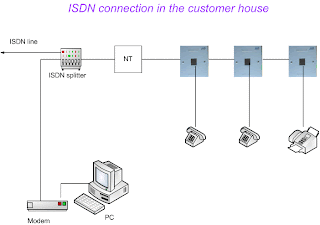
5ESS Switch :-

The class 5 electronic switching system sold by Lucent Technologies. The 5ESS Switch is the digital central office circuit switching system many communication service providers use.
5ESS has three main kinds of Module: AM is Administrative Module, which contains the central computers. CM is Communications Module, which is the central time-divided switch of the system. SM is Switching Module which in most exchanges is the majority of equipment. SM performs multiplexing, analog/digital coding, and other work to interface with the outside world. Each has a controller, a small computer whose CPUs and memories, like most common equipment of the exchange, are duplicated for redundancy.
5ESS runs on a Time-Space-Time (TST) topology. The Time-Slot-Interchangers (TSI) in the Switching Modules (SM) assign each phone call to a time slot for routing through the CM.
Distributed system lessens the load on the Central Administrative Module (AM) or main computer. AM is a dual processor mini main frame computer of the AT&T 3B series, running UNIX-RTR. AM contains the hard drives and tape drives used to load and backup the central and peripheral processor software and translations. Disk drives were originally several 300 megabyte SMD multiplatter units in a separate frame. Now they consist of several redundant multi-gigabyte SCSI drives that each reside on a card. Tape drives were originally half inch open reel at 6250 bits per inch, which were replaced in the early 1990s with 4 mm Digital Audio Tape cassettes.
Power for all circuitry is distributed as -48VDC and converted to logic or telephone voltages as needed by DC to DC converters on each shelf of circuit packs.
Switching Module (SM):-
Each SM handles several hundred to few thousand telephone lines or several hundred trunks or mixture thereof. Each has its own processors, which perform most call handling processes, using their own memory boards. Originally the peripheral processors were to be Intel 8086, but those proved inadequate and the system was introduced with Motorola 68000 series processors. The name of the cabinet that houses this equipment was changed at the same time from Interface Module to Switching Module.
T-carrier spans are terminated, one or two per card, in Digital Line Trunk Units (DLTU) which concentrate their DS0 channels into the TSI. Larger DS3 signals can also have their DS0 signals switched in Digital Network Unit SONET (DNUS) units, without demultiplexing them intoDS1. SMs have Dual Link Interface (DLI) cards to connect them by multimode optical fibers to the Communications Modules for time divided switching to other SMs. Calls among the lines and trunks of a particular SM needn't go through CM, and an SM located remotely can act as distributed switching, administered from the central AM. Each SM has two Module Controller/Time Slot Interchange (MCTSI) circuits for redundancy.
In contrast to Nortel's DMS-100 which uses individual line cards with a codec, most lines are on two stage analog space division concentrators or Line Units, which connect as many as 512 lines as needed, to the 8 Channel cards that each contain 8 codecs, and to high level service circuits for ringing and testing. Both stages of concentration are included on the same grid board. Each grid board serves 32 lines, 16 A links and 32 B links. Limited availability saves money with incompletely filled matrixes. The Line Unit can have up to 16 grid boards connecting to the channel boards by shared B links, but in offices with heavier traffic for lines a lesser number of grid boards are equipped.
Since Line Units handle the high voltages and currents of analog lines, their cards fail at higher rates than ones that handle only computer voltages. Some lines, especially ISDN or PBX ones, are served by individual line cards in an Integrated Subscriber Line Unit.
The development effort for 5ESS reached 5000 employees, producing 100 million lines of code, with 100 million lines of header and makefiles. Evolution of the system took place over 20 years, while three releases were often being developed simultaneously (each taking about 3 years to develop).
A 5ESS-2000 version, introduced in the 1990s, increased the capacity of the SM, with more peripheral modules and more optical links per SM to the CM (see below).
Administrative Module (AM):-
The Administrative Module (AM) of the 5ESS Switch is built on the 3B21D platform and is used to load software to the many microprocessors throughout the switch and to provide high speed control functions required by the AM. It provides messaging and interface to control terminals. The AM of a 5ESS consists of the 3B20x or 3B21D processor unit, including I/O, disks, and tape drive units. Once the 3B21D has loaded the software into the 5ESS and the switch is activated, packet switching takes place without further action by the 3B21D. Because the processor mirrors its functions, a failure of one side of the processor will not result in a loss of switching.
Communication Module (CM):-
The oddly named Communications Modules form the central time switch of the exchange. CMs perform time divided switching and are provided in pairs; each module (cabinet) belonging to Office Network and Timing Complex (ONTC) 0 or 1, roughly corresponding to the switch planes of other designs. Each SM has four optical fiber links, two connecting to a CM belonging to ONTC 0 and two to ONTC 1. Each optical link consists of two multimode optical fibers with screw-on connectors to plug into transceivers mounted in metal cans plugged into backplane wiring at each end. CMs receive time multiplexed signals on the receive fiber, and send them to the appropriate destination SM on the send fiber.
Very Compact Digital Exchange:-
The VCDX (Very Compact Digital eXchange) was marketed to small telephone companies and was used in some instances as a large PBX. It consisted of a single Switching Module, had no Communications Module, and used a Sun Microsystems workstation as its Administrative Module.
Signaling:-
The 5ESS has two different signaling architectures Common Network Interface (CNI) Ring and Packet Switch Unit (PSU).
Operations, Administration, Maintenance, and Provisioning:-
The system is administered through an assortment of teletypewriter "Channels" (also called the system console) such as the TEST channel and Maintenance channel. Typically provisioning is done using a one of two methods - a command line interface (CLI) called RCV:APPTEXT, and through the menu-driven RCV:MENU,APPRC program. RCV stands for Recent Change/Verification, and can be accessed throughSwitching Control Center System. Most service orders, however, are administered through Recent Change Memory Administration Center(RCMAC).